Options trading enables investors to use many different strategies to achieve their desired financial goals. The primary reasons to trade options are hedging a position, generating income, or speculating on the future price movement of an asset. In this section, we will discuss four common options trading strategies, which include Long call, Short call, Long put and Short put, as seen below:
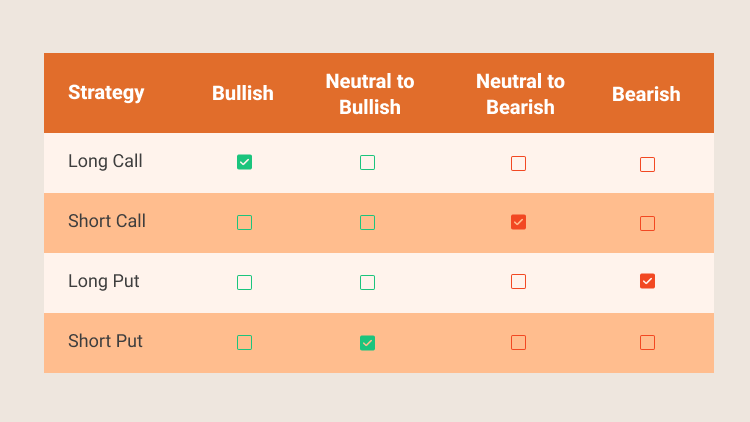
These basic options strategies can help a novice investor protect the downside and hedge market risk.
Options trading strategy: Long call
A long call is also called a buying call, which gives the buyer the right, but no obligation, to purchase shares of the underlying asset at the strike price on or before expiration. The long call strategy might be useful for an investor who is bullish on a stock price. If you think the price of an asset will rise, you can buy a call option using less capital than the asset itself. At the same time, if the price instead falls, your losses are limited to the premium paid for the options and no more.
- Example of long call strategy
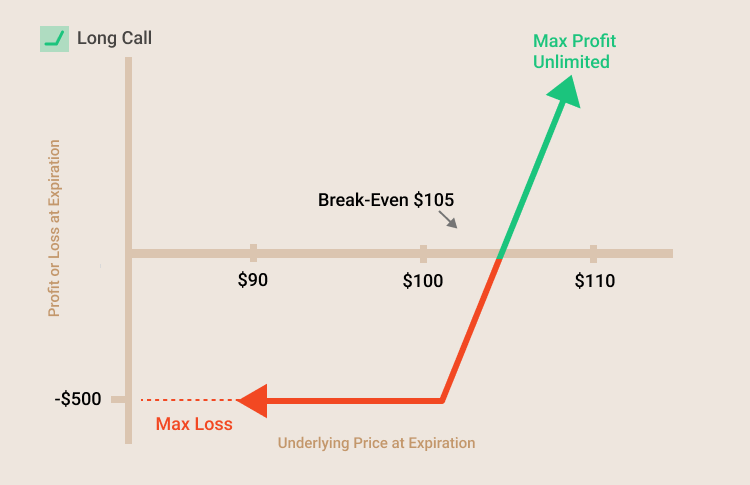
Consider a call option with a premium of $5 and a strike price of $100. This means the buyer pays $5 to the writer. At expiration, if the price of the stock is less than or equal to the $100 strike price (the option has zero value), the buyer of the option is out $5, and the writer of the option is ahead $5. As the stock’s price exceeds $100, the buyer of the option starts to gain (breakeven will come at $105, when the value of the stock equals the strike price and the option premium). However, as the price of the stock moves upward, the seller of the option starts to lose.
Options trading strategy: Long put
A long put allows an investor to pay a fixed premium for the right, but not the obligation, to sell an asset at a predetermined price until expiration. This strategy might be useful for an investor who is bearish on a stock price. Investors going long puts may profit if the price of the underlying shares falls below the combined value of the strike price and the net cost of the option. However, if the stock goes up, you don’t have to deliver shares. Meanwhile, investors use puts as an alternative to short stock, but their risk is limited to the cost of the option contracts.
- Example of long put strategy
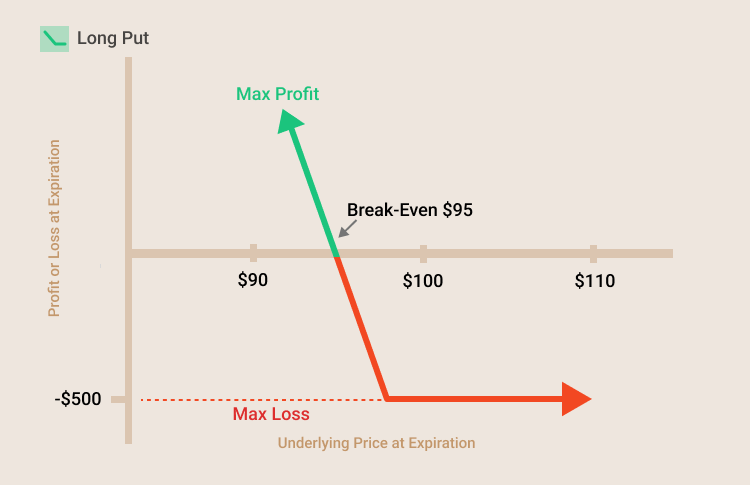
Let‘s say a long put with a $5 premium, and the buyer pays $5 to the writer. When the price of the stock at expiration is greater than or equal to the $100 strike price, the put option has zero value, the buyer of the option has a loss of $5 premium, and the writer of the option has a gain of $5. As the stock’s price falls below $100, the buyer of the put option starts to gain (breakeven will come at $95 when the value of the stock equals the strike price minus the option premium). However, as the price of the stock moves downward, the seller of the option starts to lose (negative profits will start at $95, when the value of the stock equals the strike price less the option premium).
Options trading strategy: Short call
A call option gives the buyer of the option the right to purchase underlying shares at the strike price before the contract expires. When an investor sells a call option, the transaction is called a short call. A short call is when a trader believes that the price of the asset underlying the option will drop, so it is considered a bearish trading strategy.
The success of the short call strategy rests on the option contract expiring worthless. That way, the trader banks the profit from the premium. For this to happen, the price of the underlying security must fall below the strike price. If it does, the buyer won't exercise the option.
If the price rises, the option will be exercised because the buyer can get the shares at the strike price and immediately sell them at the higher market price for a profit. In this case, the seller has unlimited exposure because the underlying asset price could rise above the strike price during this time, and keep rising.
- Example of short call strategy
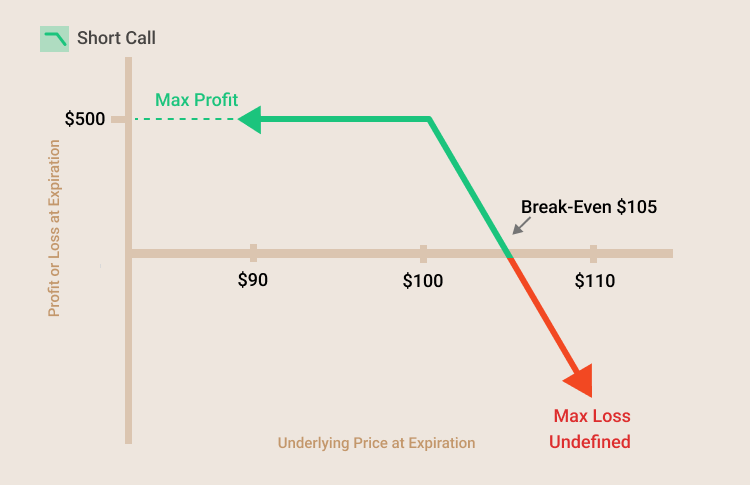
If a short call option with a strike price of $100 is sold for a $5 premium, the maximum profit potential is $500. The maximum loss is undefined above the break-even point. The strike price plus the premium equals the break-even price of $105. If the underlying stock price is above the break-even point at expiration, the position will result in a loss.
Options trading strategy: Short put
A short put is the sale of a put option. When shorting a put option, the seller has the right to sell short the option’s underlying stock at the strike price and expiration date. The trader who buys the short put option is long that option, and the trader who wrote that option is short. Short puts are profitable if the underlying asset's price is above the strike price at expiration, so it is considered a bullish option strategy with limited profit potential. In addition, the profit on a short put is limited to the premium received, but the risk can be significant. When writing a put, the writer is required to buy the underlying at the strike price. If the price of the underlying falls below the strike price, the put writer could face a significant loss.
- Example of short put strategy
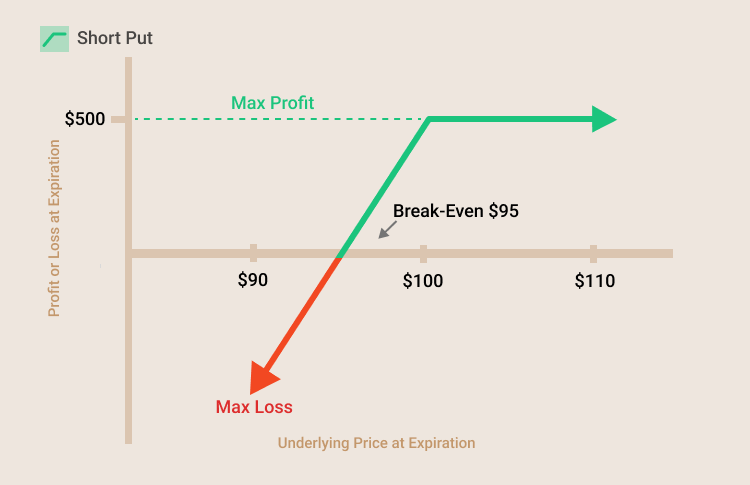
If a short put option with a strike price of $100 is sold for $5 premium, the maximum profit potential is $500. The maximum loss is undefined below the break-even point. The strike price minus the premium equals the break-even price of $95. If the underlying stock price is below the break-even point at expiration, the position will result in a loss.
Summary:
- There are four basic options trading strategies, which include Long call, Short call, Long put and Short put.
- A long call is a bullish strategy which gives the buyer the right, but no obligation, to purchase shares of the underlying asset at the strike price on or before expiration.
- A long put is a bearish strategy which allows an investor to pay a fixed premium for the right, but not the obligation, to sell an asset at a predetermined price until expiration.
- When an investor sells a call option, the transaction is called a short call. A short call is when a trader believes that the price of the asset underlying the option will drop, so it is considered a bearish trading strategy.
- A short put is the sale of a put option. When shorting a put option, the seller has the right to sell short the option’s underlying stock at the strike price and expiration date. Short puts are profitable if the underlying asset's price is above the strike price at expiration, so it is considered a bullish option strategy with limited profit potential.



